*The below article contains affiliate links which means that if you make a purchse after clicking on on I may earn a commission at no extra cost to you.
A foodscape refers to the practice of growing food in a landscape setting, combining both ornamental and edible plants. Gardening in arid climates presents unique challenges due to the scarcity of water. Water conservation is crucial in gardening to ensure the sustainability of our resources and to mitigate the effects of climate change.
In arid climates, water is a precious resource that needs to be used efficiently. The lack of rainfall and high temperatures make it difficult for plants to thrive without proper care and attention. Therefore, it is essential to adopt water-efficient practices in foodscape gardening to ensure the success of the project.
Key Takeaways
- Water-efficient foodscape is important in arid climates to conserve water resources.
- Urban foodscaping involves growing food in urban areas to promote sustainability and self-sufficiency.
- Sustainable practices in foodscape include using organic gardening methods and choosing the right plants for edible landscaping.
- Water-saving techniques for community gardening include mulching, drip irrigation, and rainwater harvesting.
- Designing a water-efficient foodscape involves considering factors such as soil type, sun exposure, and water availability, and choosing appropriate irrigation systems.
Understanding Urban Foodscaping
Urban foodscape refers to the practice of growing food in urban areas, such as rooftops, balconies, and community gardens. It is a way to bring agriculture back into cities and promote sustainable living. Urban foodscape projects have numerous benefits, including increased access to fresh and healthy food, improved air quality, and enhanced community engagement.
One example of an urban foodscape project is the Brooklyn Grange Rooftop Farm in New York City. It is one of the largest rooftop farms in the world, spanning over two acres. The farm grows a variety of vegetables and herbs using organic practices. Another example is the Edible Schoolyard Project in Berkeley, California, which transforms schoolyards into productive gardens where students can learn about food production and healthy eating.
Importance of Sustainable Practices in Foodscape
Sustainable practices in foodscape gardening refer to methods that minimize environmental impact and promote long-term ecological balance. These practices include organic gardening, composting, and using natural pest control methods. By adopting sustainable practices, we can reduce our reliance on synthetic chemicals and protect the health of our soil, water, and wildlife.
The benefits of sustainable practices in foodscape gardening are numerous. Organic gardening, for example, promotes soil health and biodiversity by avoiding the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. Composting helps to recycle organic waste and enrich the soil with nutrients. Natural pest control methods, such as companion planting and attracting beneficial insects, reduce the need for harmful chemical pesticides.
Organic Gardening in Arid Climates
| Topic | Metric | Data |
|---|---|---|
| Soil | pH level | 6.5-7.5 |
| Watering | Frequency | Once a week |
| Composting | Ratio | 3:1 (brown:green) |
| Planting | Season | Fall and Spring |
| Pest Control | Natural remedies | Neem oil, garlic spray, ladybugs |
Organic gardening refers to the practice of growing plants without the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, or genetically modified organisms (GMOs). In arid climates, organic gardening is particularly important as it helps to conserve water and protect the fragile ecosystem.
The benefits of organic gardening in arid climates are numerous. Organic practices promote soil health and fertility, allowing plants to better withstand drought conditions. By avoiding synthetic chemicals, organic gardening also protects the quality of groundwater and reduces pollution. Additionally, organic gardening encourages biodiversity by providing habitat for beneficial insects and wildlife.
To practice organic gardening in arid climates, it is important to choose drought-tolerant plants that can thrive with minimal water. Mulching is also essential to conserve moisture in the soil and suppress weed growth. Composting is another key practice in organic gardening as it helps to improve soil structure and water-holding capacity.
Choosing the Right Plants for Edible Landscaping
When selecting plants for edible landscaping in arid climates, it is important to consider several factors. First, choose plants that are native or well-adapted to the local climate and soil conditions. These plants are more likely to thrive with minimal water and maintenance.
Some examples of plants that thrive in arid climates include succulents like agave and aloe vera, herbs like rosemary and lavender, and fruit trees like pomegranate and fig. These plants have evolved to survive in dry conditions and can tolerate periods of drought.
It is also important to consider the water requirements of different plants. Grouping plants with similar water needs together can help to optimize water usage and reduce waste. Additionally, consider using drip irrigation or other water-efficient methods to deliver water directly to the roots of plants, minimizing evaporation and runoff.
Water-Saving Techniques for Community Gardening

Community gardening refers to the practice of growing food collectively in a shared space. It is a way to promote community engagement, improve food security, and enhance the beauty of urban areas. In arid climates, water-saving techniques are crucial for the success of community gardening projects.
One water-saving technique for community gardening is the use of mulch. Mulching helps to retain moisture in the soil, reduce weed growth, and regulate soil temperature. Organic mulches like straw or wood chips are particularly effective in conserving water.
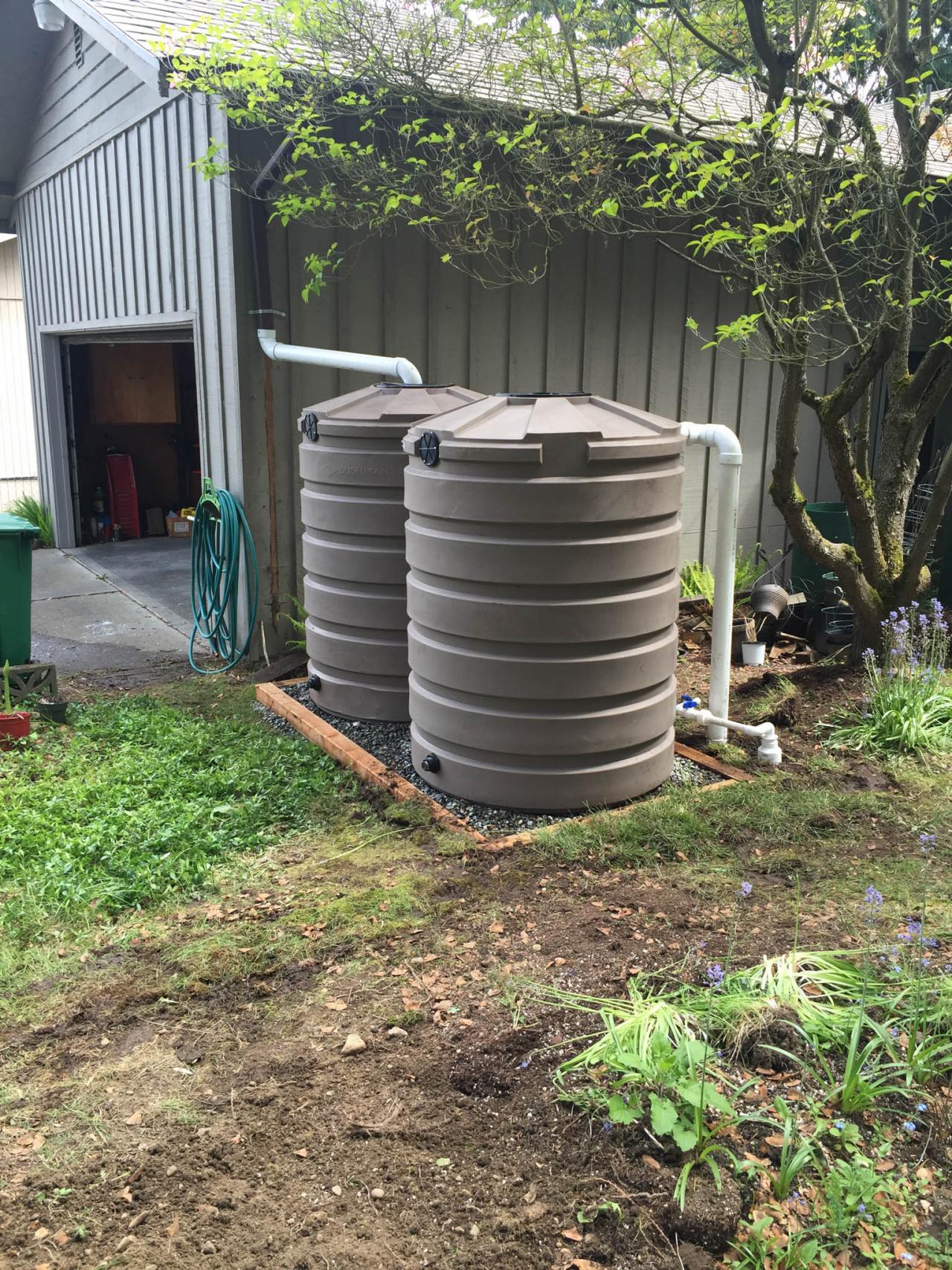
Another technique is the use of rainwater harvesting systems. By collecting rainwater from rooftops or other surfaces, community gardens can reduce their reliance on municipal water supplies. Rainwater can be stored in tanks or barrels and used for irrigation during dry periods.
Designing a Water-Efficient Foodscape
When designing a water-efficient foodscape, it is important to consider several factors. First, assess the site’s microclimate and soil conditions to determine the best location for different plants. Some areas may receive more shade or have better soil drainage, which can affect plant selection and water requirements.
Incorporating water-efficient features like rain gardens or bioswales can help to capture and filter rainwater, reducing runoff and replenishing groundwater supplies. These features can also provide habitat for beneficial insects and wildlife.
Using permeable paving materials can also help to reduce stormwater runoff and allow rainwater to infiltrate into the soil. This helps to recharge groundwater supplies and reduce the strain on municipal water systems.
Irrigation Systems for Arid Climates
In arid climates, choosing the right irrigation system is crucial for the success of a foodscape project. There are several types of irrigation systems that are suitable for arid climates, including drip irrigation, micro-sprinklers, and soaker hoses.
Drip irrigation is a water-efficient method that delivers water directly to the roots of plants, minimizing evaporation and runoff. It is particularly effective for watering individual plants or rows of plants. Micro-sprinklers are another option, which deliver water in a fine mist or spray. Soaker hoses are porous hoses that release water slowly and evenly along their length.
When selecting an irrigation system, consider the water requirements of different plants and group them together accordingly. This allows for more efficient water usage and reduces waste. Additionally, consider using a timer or moisture sensor to automate the irrigation system and ensure that plants receive the right amount of water at the right time.
Harvesting and Storing Rainwater for Foodscape
Harvesting and storing rainwater is an effective way to conserve water in a foodscape project. Rainwater is free and abundant, and collecting it can help to reduce reliance on municipal water supplies.
To harvest rainwater, install gutters and downspouts on rooftops to direct rainwater into storage tanks or barrels. These containers should be covered to prevent mosquito breeding and contamination. The collected rainwater can then be used for irrigation during dry periods.
It is important to store rainwater properly to prevent evaporation and contamination. Use dark-colored containers or cover them with a dark material to reduce sunlight exposure and algae growth. Additionally, consider installing a filter or screen to remove debris before the water enters the storage container.
Maintenance and Care for a Water-Efficient Foodscape
Maintaining a water-efficient foodscape requires ongoing care and attention. Regularly monitor soil moisture levels and adjust irrigation accordingly. Mulch should be replenished as needed to maintain its effectiveness in conserving moisture and suppressing weeds.
Prune plants regularly to promote healthy growth and prevent overcrowding. Remove any dead or diseased plants to prevent the spread of pests and diseases. Additionally, monitor for pests and use natural pest control methods, such as handpicking or introducing beneficial insects.
It is also important to regularly inspect and maintain irrigation systems. Check for leaks, clogs, or other issues that may affect the efficiency of the system. Clean filters and nozzles as needed to ensure proper water flow.
In conclusion, water-efficient foodscape gardening in arid climates is essential for conserving water and promoting sustainable practices. By understanding the challenges of gardening in arid climates and adopting water-saving techniques, we can create beautiful and productive landscapes while minimizing our impact on the environment. With careful planning and ongoing care, a water-efficient foodscape can thrive and provide a sustainable source of fresh and healthy food.
If you’re interested in creating a water-efficient foodscape in arid climates, you may also want to check out the article on “Eco-Friendly Living” on Growr.app. This article provides valuable tips and insights on how to live a more sustainable and environmentally friendly lifestyle. From conserving water to reducing waste, it offers practical advice that can help you make a positive impact on the planet. So, if you’re looking for more ways to incorporate eco-friendly practices into your foodscape project, be sure to give it a read!
FAQs
What is a water-efficient foodscape?
A water-efficient foodscape is a landscape design that incorporates edible plants and is designed to minimize water usage.
Why is it important to create a water-efficient foodscape in arid climates?
Arid climates have limited water resources, and creating a water-efficient foodscape can help conserve water while still allowing for the cultivation of edible plants.
What are some examples of edible plants that can be grown in a water-efficient foodscape?
Examples of edible plants that can be grown in a water-efficient foodscape include cacti, succulents, herbs, and fruit trees that are adapted to arid climates.
What are some strategies for creating a water-efficient foodscape?
Strategies for creating a water-efficient foodscape include selecting drought-tolerant plants, using mulch to retain moisture, incorporating rainwater harvesting systems, and using efficient irrigation methods.
What are the benefits of creating a water-efficient foodscape?
Benefits of creating a water-efficient foodscape include conserving water resources, reducing water bills, providing fresh and healthy food, and creating a beautiful and sustainable landscape.